Introduction
Day to day business operations already provide enough strain for your workforce, however cybercriminals don’t care. The additional threat of cybercrime is now a painful reality. According to the government’s cyber security breaches survey 2024, half of businesses (50%) and around a third of charities (32%) report having experienced some form of cyber security breach or attack in the last 12 months. This is much higher for medium businesses (70%), large businesses (74%) and high-income charities with £500,000 or more in annual income (66%). Notwithstanding any investment in risk mitigation, it makes sense to prepare for the worst. Being able to quickly assess the magnitude of any exposure in these breaches is crucial.
Challenges
History tells us, cyberbreaches require the rapid identification of the exposed data (whether that be PII, login information or other sensitive datatypes), to quickly understand what and to plan for what happens next, and to mitigate material risk.
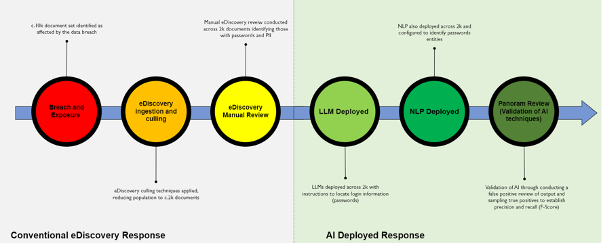
Conventional thinking and a conventional solution would be to execute a standard forensic and eDiscovery approach, i.e. to run keyword and other analytics tools to identify the mission critical documents, and have humans review the documents to confirm and identify. This provides a robust assessment with a reasonable degree of accuracy, but depending on the size of the data set can take many days, even weeks with dedicated review teams and is frankly an unbudgeted expense. Not only that, as each day the investigation and response drags on, the risk multiplies.
However, when considering certain sensitive information, it’s nigh on impossible to restrict to a set of standardised keyword terms, given these are not particularly search or regex-friendly and are present in a variety of random structures. Let’s take passwords, these by their very nature have unlimited variance, the simplest (and of course not safest) passwords such as; Password123 all the way to a highly secure password using mixtures of characters, cases and symbols; oA&gS+F77W2p4KBfo8^ both pose technical challenges for conventional eDiscovery technology.
AI is the answer (of course)
The solution, when reacting to a cyberbreach is undoubtedly speed and accuracy. Through the deployment of a two-pronged AI approach, (Large Language Model – LLM, Natural Language Processing – NLP), these tools identify the critical dataset, exposed sensitive information, with comparative ease to the conventional eDiscovery methods.
For LLMs, prompt engineering is critical. Using the RISEN (Role, Input, Steps, Expectation, Narrowing) framework, Panoram specialists create multilayered prompt queries, with a methodology to iteratively refine across multiple runs.
In parallel, NLP techniques can be deployed, in particular the creation of a “Magnitude Report”. This is a succinct and actionable assessment with a breakdown of recognised sensitive data entities. Outputs from both technologies are then promoted to an eDiscovery review tool, and residual false positives can be excluded.
To test the validity of this approach and in the interest of comparison (and frankly curiosity), more traditional and rudimentary eDiscovery review can serve useful for benchmarking the efficacy of the AI. It is not uncommon in human eDiscovery review to miss up to 10% of documents with sensitive information across a dataset. Human review teams often miss identifying sensitive information because it is difficult for the human eye to pick up in large multi-page documents.
Evidently, a multi-technology approach identifies the heart of the issue with greater speed and accuracy, than conventional eDiscovery review. The rapid identification of potentially affected documents will enable a breached organisation to act swiftly and to contain the exposure. AI delivers the outcome and allows for the issue to be assessed and quantified, enabling quick and thorough response and remediation.
Project Validation
Panoram’s findings show AI outperforms humans, making typical eDiscovery review increasingly redundant. That being said, a solid grounding in eDiscovery makes this workflow possible, and it is paramount to understand why the AI performs as it does, something that eDiscovery has offered since inception- “Show your working”. It could be argued the workings as to how an LLM gets an answer remain enigmatic, so, to validate its output, in a recent case study we performed statistical analysis and human sample review of the AI generated outputs, considering precision and recall (F-Score) as a means of quality assurance for the overall approach and to satisfy the client affected data has been identified and isolated.
Conclusions
The speed and accuracy of a response for cyberbreaches will define the impact to the breached organisation from a containment, remedy, and regulatory perspective. However, Cyber criminals have the same access to the same tech and are not only getting more sophisticated in their attacks but are now more non-discriminatory than ever, targeting businesses of any size and sector. A robust cyber breach response such as the below will ensure your organisation is best equipped should the worst occur.
Panoram eDiscovery Cyberbreach Workflow using AI: